The condition:
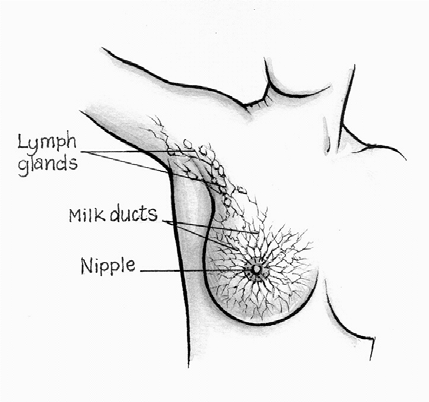
The breast is a glandular tissue (can secrete
substances). Around the breast are lymph
nodes. These are part of the lymphatic system.
Lymphatic vessels run from the limbs towards
the heart, usually beside veins. They carry fluid
called lymph, which is a collection of dead
cells, waste material and leakage from ordinary
blood vessels.
At various points along a lymphatic vessel lie
lymph nodes. These are usually small – 5mm or
less in most places. Lymph nodes are
scattered at various points around the body,
but the most important ones for breast disease
are in the armpit.
Cancer cells travel along lymphatic vessels and
collect in lymph nodes. In breast cancer, the
lymph nodes of the armpit are usually the first
site of spread.
The operation:
It is important to understand that breast surgery
for cancer is not cosmetic surgery. The
appearance of the breast after surgery will be
different from that before surgery.
The survival rates for women who have
mastectomy (all of the breast removed) are the
same as for women who have breastconserving
surgery accompanied by
radiotherapy, and each form of treatment has
its advantages.
Wide local excision
The removal of a lump in the breast and the
tissue around it. The lymph nodes under the
arm on the same side as the tumour may also
be removed and tested for cancer. If the lump
can not be felt, a marking wire may need to be
placed before surgery. This is usually done in
the X-Ray department using ultrasound or
mammogram.
Partial or segmental mastectomy
The removal of the tumour as well as some of
the breast tissue around it and the lining over
the chest muscles below. Usually some of the
lymph nodes under the arm are taken out and
tested for possible spread of cancer.
Total or simple mastectomy
The removal of the whole breast. Sometimes
lymph nodes under the arm are also taken out
and tested for possible spread of cancer.
Modified radical mastectomy
The removal of the breast, many of the lymph
nodes under the arm, the lining over the chest
muscles, and sometimes part of the chest wall
muscles.
Radical mastectomy
The removal of the breast, chest muscles, and
all of the lymph nodes under the arm. It is used
only when the tumour has spread to the chest
muscles.
Reconstruction
Breast reconstruction involves the use of
prostheses (artificial breast tissue) or tissue
from other parts of the body. The type of
prosthesis can be either silicone filled but are
usually saline filled implants. Soft tissue may
be taken from the other breast, the back or
abdomen depending on body shape and size.
Risks of this procedure:
There are some risks/ complications.
(a) Infection in the operation site causing pain,
swelling, redness and discharge and the wound
may break down. Treatment may be wound
dressings, drainage and antibiotics.
(b) The operation site under the arm continues to
ooze fluid. This may need to be drained with a
needle and syringe.
(c) The edges of the wound may lose blood supply
and change colour. Further surgery may be
needed to cut out the affected areas along the
wound.
(d) Weakness and numbness of the arms and chest
may happen due to certain nerves being cut
during the operation.
(e) Difficulty with arm movement due to shoulder
stiffness after the operation.
(f) The layers of the wound may not heal
adequately and the wound may burst open.
(g) The wound may not heal normally. The scar can
be thickened and red and may be painful.
(h) Swelling of the arm (lymphoedema) on the side
of the operation.
(i) Recurrence of tumour in or around the scar
which will need further treatment to remove or to
destroy the tumours.
(j) Chronic pain after mastectomy in the area of the
surgery. It is usually managed with drugs
prescribed by pain specialist.
(k) Feelings of anxiety and depression due to the
disease and possible recurrence.
(l) Feelings of anxiety and depression due to losing
a breast.
(m) Loss of sexuality due to distress at the change in
body image or depression due to the disease.
(n) Increased risk in obese people of wound
infection, chest infection, heart and lung
complications, and thrombosis
(o) Increased risk in smokers of wound and chest
infections, heart and lung complications and
thrombosis.
